In this video, I demonstrate how to find the antiderivative or the integral of tan^2(x) This would normally be quite a difficult integral to solveHowever,Solve for x tan (2x)=1 tan (2x) = 1 tan ( 2 x) = 1 Take the inverse tangent of both sides of the equation to extract x x from inside the tangent 2x = arctan(1) 2 x = arctan ( 1) The exact value of arctan(1) arctan ( 1) is π 4 π 4 2x = π 4 2 x = π 4 Divide each term by 2Solve (2tanx)/(1 tan ^2 x) Get the answer to this question and access a vast question bank that is tailored for students
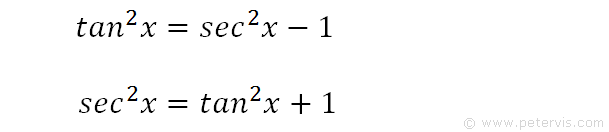
Integrate Sec 2x Method 1
Tan 2xcosx
Tan 2xcosx-Simplifying tan 2 (x) 3tan(x) * 2 = 0 Multiply an 2 t * x an 2 tx 3tan(x) * 2 = 0 Reorder the terms for easier multiplication an 2 tx 3 * 2ant * x = 0 Multiply 3 * 2 an 2 tx 6ant * x = 0 Multiply ant * x an 2 tx 6antx = 0 Reorder the terms 6antx an 2 tx = 0 Solving 6antx an 2 tx = 0 Solving for variable 'a' Move all termsOur given expression is tan(2x y) tan(2x – y) = 1 Formula used When A B = 90° then, tanA tanB = 1 and vice versa Calculation Our given expression is tan(2x y) tan(2x – y) = 1 ⇒ 2x y 2x – y = 90° ⇒ 4x = 90° ⇒ 2x = 45° Now, tan2x = tan45° = 1 ∴ The value of tan45° is 1 Download Question With Solution PDF ››




Solve Tan 2x Tanx 0
differentiate using the chain rule given y = f (g(x)) then dy dx = f '(g(x)) × g'(x) ← chain rule y = (tanx)2 ⇒ dy dx = 2tanx × d dx (tanx) ⇒ dy dx = 2tanxsec2x Answer link The Second Derivative Of tan^2x To calculate the second derivative of a function, differentiate the first derivative From above, we found that the first derivative of tan^2x = 2tan(x)sec 2 (x) So to find the second derivative of tan^2x, we need to differentiate 2tan(x)sec 2 (x) We can use the product and chain rules, and then simplify to find the derivative of 2tan(x)sec 2 (xSimply note that the following identity holds tan 2 x = 1 − t a n 2 x 2 t a n x which can be easily checked by the following tan 2 x = c o s 2 x s i n 2 x sin 2 x = 2 sin x cos x cos 2 x = cos 2 x − sin 2 x
Identity\\tan(2x) multipleangleidentitiescalculator identity \tan(2x) en Related Symbolab blog posts High School Math Solutions – Trigonometry Calculator, Trig Identities In a previous post, we talked about trig simplification Trig identities are very similar to this concept An identity Example 22 Find the derivative of tan (2x 3) Let y = tan (2x 3) We need to find derivative of y, ie 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑 tan〖(2𝑥3)〗)/𝑑𝑥 = sec2(2x 3) × (𝑑(2𝑥 3))/𝑑𝑥 = sec2 (2x 3) × 2 = 2 sec2 (2x 3) (As (tan x)' = sec2 x) Show MoreTo prove tan 3x tan 2x tan x = tan 3x – tan 2 x – tan x We know that 3x can be written as 2xx Hence, tan 3x = tan (2xx) By using the trigonometric identity, the above expression is written as Tan 3x = (tan 2x tanx)/ (1tan 2x tanx) Now, cross multiply above expression, we get Tan 3x – tan 3x tan 2x tan x = tan 2x tan x
Mathtan^2xcot^2x=2/math math\therefore tan^2x\dfrac{1}{tan^2x}2=22/math math\therefore \left(tanx\dfrac{1}{tanx}\right)^2=4/math math\thereforeGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us! Get an answer for '`tan(2x) cot(x) = 0` Find the exact solutions of the equation in the interval 0, 2pi)' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotes




Answered Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x From Bartleby




Dy Dx Y Tan2x Edurev Clat Question
Integral of tan^2x, solution playlist page http//wwwblackpenredpencom/math/Calculushtmltrig integrals, trigonometric integrals, integralThe period of the tan(2x) function is π 2 so values will repeat every π 2 radians in both directions x = π 8 πn 2, 5π 8 πn 2, for any integer nIntegral of tan^2 (x) \square!




Int Tan X Tan 2x Tan 3x Dx Youtube
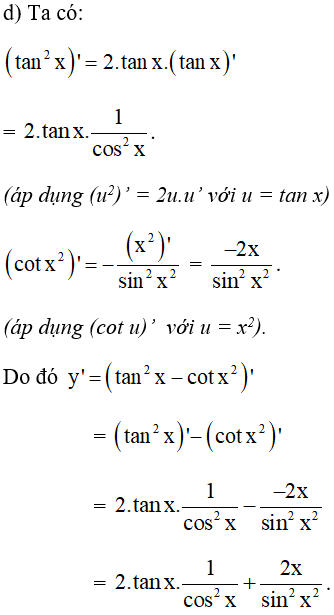



Tim đạo Ham Của Cac Ham Số Sau Y Tan 2 X Cot X 2 Vietjack Com
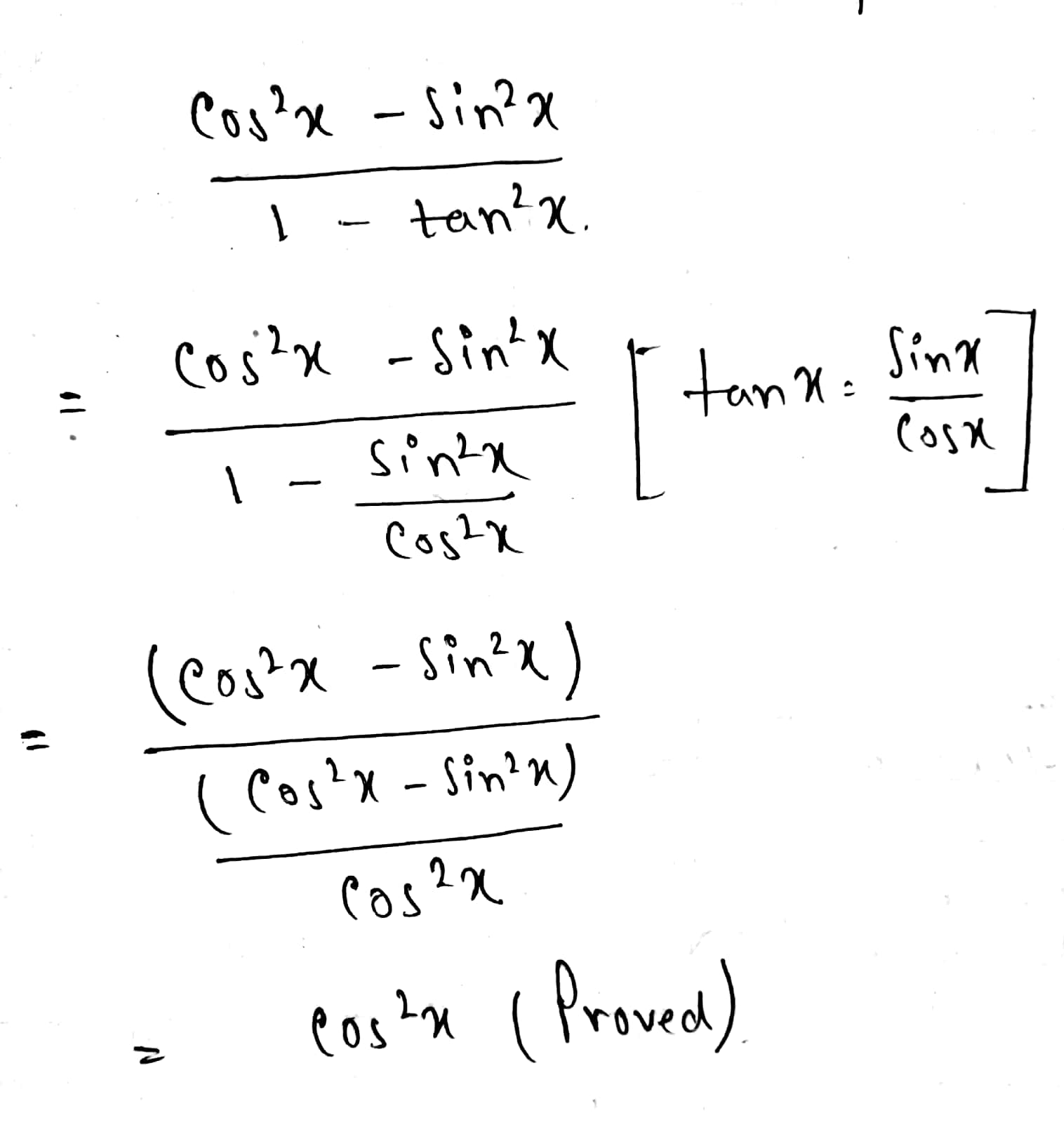
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators When trying to prove trig identities, it is often helpful to convert TAN functions into SIN/COS functions Proof Step 1 Start with the original equation to prove tan 2 x sin 2 x = (tan 2 x)(sin 2 x) Proof Step 2 Replace tan with sin/cos (sin 2 x/cos 2 x) sin 2 x = (sin 2 x/cos 2 x)(sin 2 x) Proof Step 3 Obtain a common denominator on left, simplify right (sin 2 x sin 2 x cos 2 x using the trigonometric identities ∙ xtanx = sinx cosx ∙ xsin2x cos2x = 1 consider the left side take out a common factor tan2x tan2x(1 − sin2x) = sin2x cos2x × cos2x = sin2x = right side ⇒ verified Answer link



C2 Solve Tan2x 0 In The Interval 0 180 The Student Room
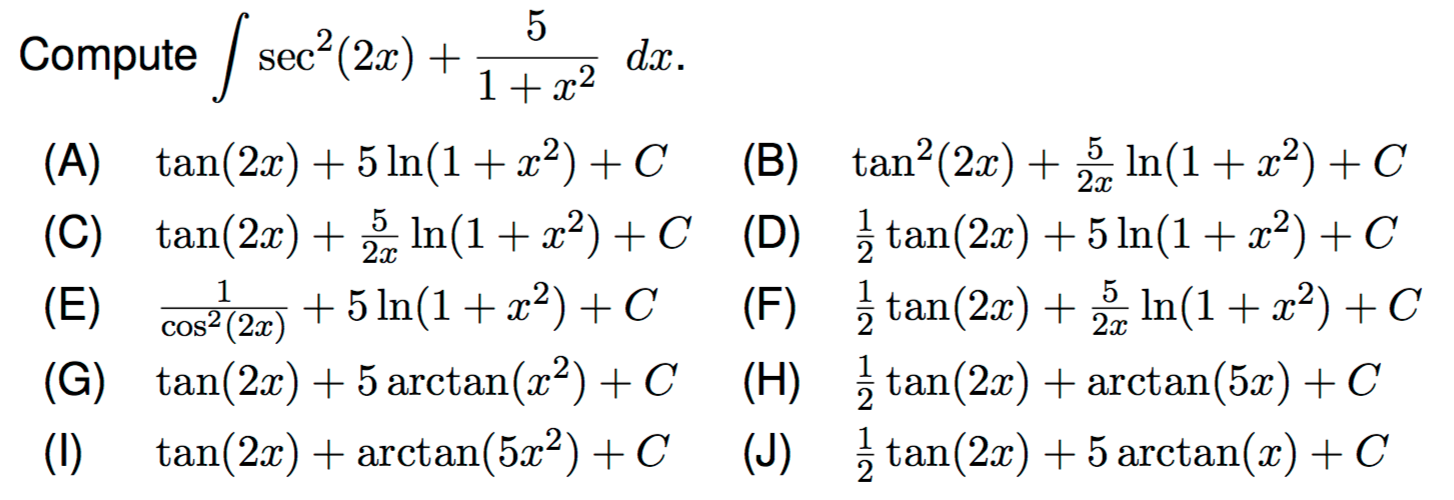



Compute Sec 2 2x 5 1 X 2 Dx A Tan 2x 5 Ln L Chegg Com
Solution 2x = 5x – 3x Taking "tan" on both sides, tan 2x = tan (5x – 3x) tan 2x = (tan 5x – tan 3x)/ (1 tan 5x tan 3x) tan 2x (1 tan 5x tan 3x) = tan 5x – tan 3x tan 2x tan 5x tan 3x tan 2x = tan 5x – tan 3x tan 5x tan 3x tan 2x = tan 5x – tan 3x – tan 2xGet an answer for 'Prove tan^2x sin^2x = tan^2x sin^2x' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesCos 2x ≠ 2 cos x;




Prove That Tan 2 2x Tan 2 X1 Tan 2 2x Tan 2 X Tan 3x Tan X




Tanx Tan2x Tan3x 0
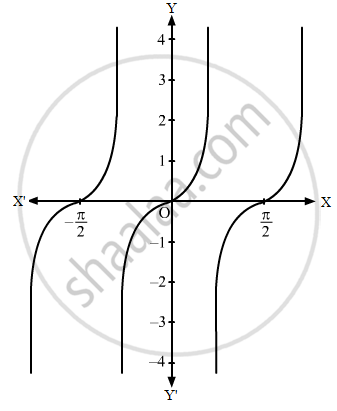
Tan^2x = 3 then tanx = √ 3 and tanx =√ 3 when tanx =√ 3 then x = π /3 and x = 4π /3 and when x = √ 3 then x = 2π /3 and 5π /3 these are the solution for x in given interval 0 2π 2sec^2(2x) Assuming that you know the derivative rule d/dx(tanx)=sec^2(x) d/dx(tan(2x)) will simply be sec^2(2x)* d/dx(2x) according to the chain rule Then d/dx(tan(2x))=2sec^2(2x) If you want to easily understand chain rule, just remember my tips take the normal derivative of the outside (ignoring whatever is inside the parenthesis) and thenThe vertical asymptotes for y = tan ( 2 x) y = tan ( 2 x) occur at − π 4 π 4, π 4 π 4, and every π n 2 π n 2, where n n is an integer Tangent only has vertical asymptotes Use the form atan(bx−c) d a tan ( b x c) d to find the variables used to find the amplitude, period, phase shift, and




Example 22 Solve Tan 2x Cot X Pi 3 Teachoo Examples
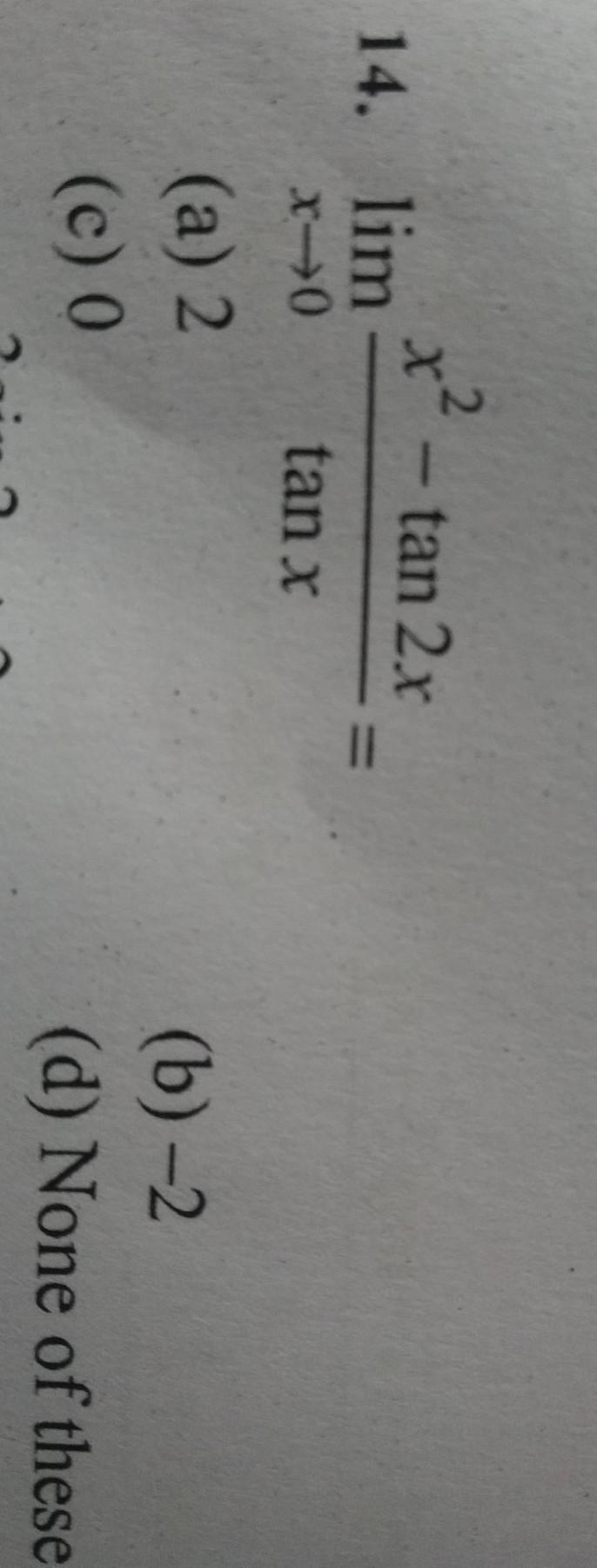



2 X Tan 2x Tan X 14 Lim X 0 A 2 C O B 2 D No Math
How to integrate tan^2 x In numerator, you may use series expansion of tan x = x x 3 3 You need not write next terms as the denominator has degree 4 So, more powers of x in numerator would make it zero With this approach also, you would get answer as 2 3 Detailed steps lim x → 0 ( x x 3 3) 2 − x 2 x 4 = lim x → 0 x 2 2 x 4 3 − x 2 x 4 = 2 3 Example 22 Solve tan 2x = – cot (x" " 𝜋/3) tan 2x = –cot (𝑥" " 𝜋/3) We need to make both in terms of tan Rough tan (90° θ) = –cot θ –cot θ = tan (90° θ) –cot θ = tan (𝜋/2 " θ" ) Replacing θ by x 𝜋/3 –cot ("x " 𝜋/3) = tan (𝜋/2 " x " 𝜋/3) tan 2




The General Solution Of The Equation Tanx Tan2x Tanx Tan2x 1 Is Youtube




Zenbot
Trigonometric Formulas like Sin 2x, Cos 2x, Tan 2x are known as double angle formulas because these formulas have double angles in their trigonometric functions Let's discuss Tan2x Formula Tan2x Formula = 2 tan x 1 − t a n 2 x Let's know how to derive the double angle tan2x formulaGet an answer for 'Prove that tan^2x/(1tan^2x) = sin^2x' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesEvaluate {eq}\displaystyle \int (2 x 4x^3 \tan^2 x 1)\ dx {/eq} Indefinite integral An indefinite integral is also referred to as the primitive integral, inverse derivative, antiderivative



3
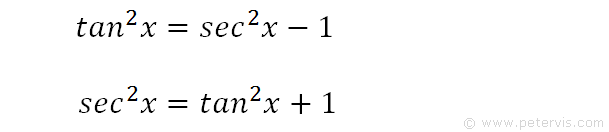



Integrate Sec 2x Method 1
Tan (2x) is a doubleangle trigonometric identity which takes the form of the ratio of sin (2x) to cos (2x) sin (2x) = 2 sin (x) cos (x) cos (2x) = (cos (x))^2 – (sin (x))^2 = 1 – 2 (sin (x))^2 = 2 (cos (x))^2 – 1 Proof 71K views View upvotes View shares Example 14 Show that tan 3𝑥 tan 2𝑥 tan 𝑥 = tan 3𝑥 – tan 2𝑥 – tan 𝑥 We know that 3𝑥 = 2𝑥 𝑥 Therefe, tan 3𝑥 = tan(2𝑥 𝑥Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more




Get Answer 1 Tan2x Sec2x Dx Sin2x 2 C Tan 2 X 2 C 2sin X Cos X Transtutors




Verify That The Equation Is An Identity Tan 2x Cot Chegg Com
Tan^2 (x) WolframAlpha Volume of a cylinder?Derive the expression 1 tan^2x Get the answer to this question and access a vast question bank that is tailored for students f (g (x)) = tan (2x) ⇒ f' (g (x)) = sec2(2x) = 2sec 2 (2x) Using the chain rule, the derivative of tan (2x) is 2sec2(2x) Finally, just a note on syntax and notation tan (2x) is sometimes written in the forms below (with the derivative as per the calculation above) Just be aware that not all of the forms below are mathematically correct tan2x
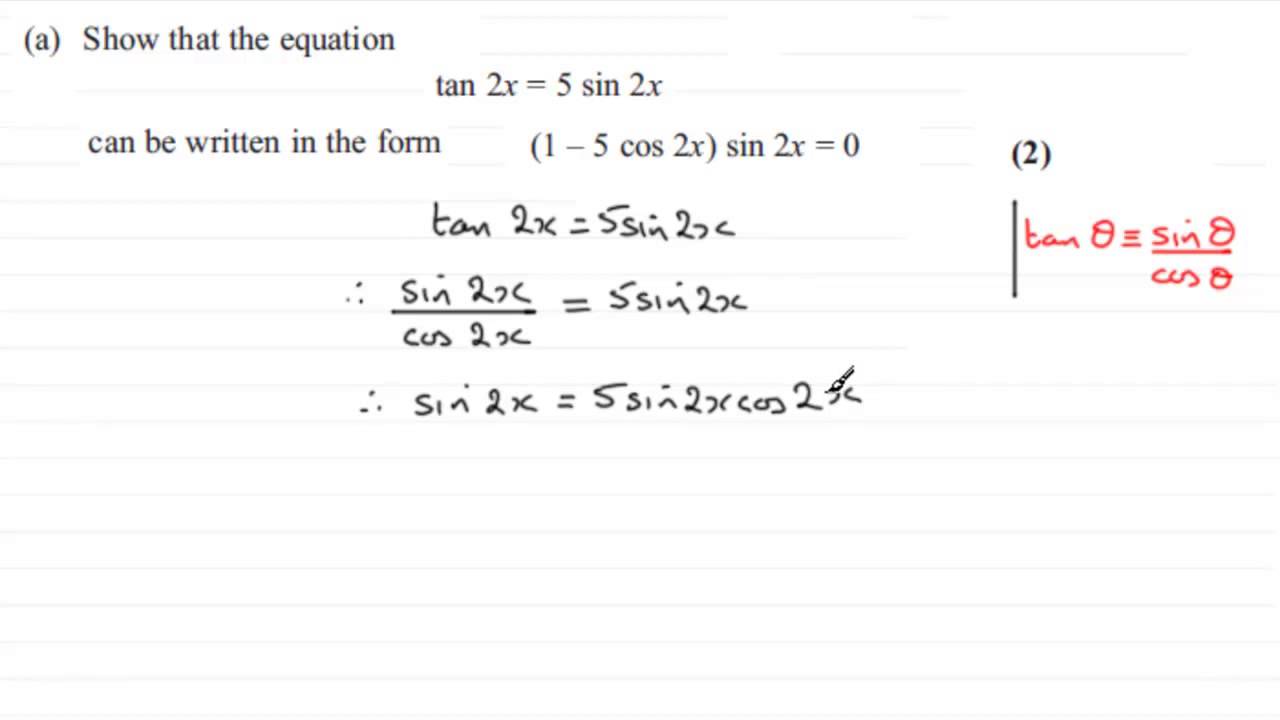



Edexcel Core Mathematics C2 June 12 Solutions Examples Worksheets Videos Activities
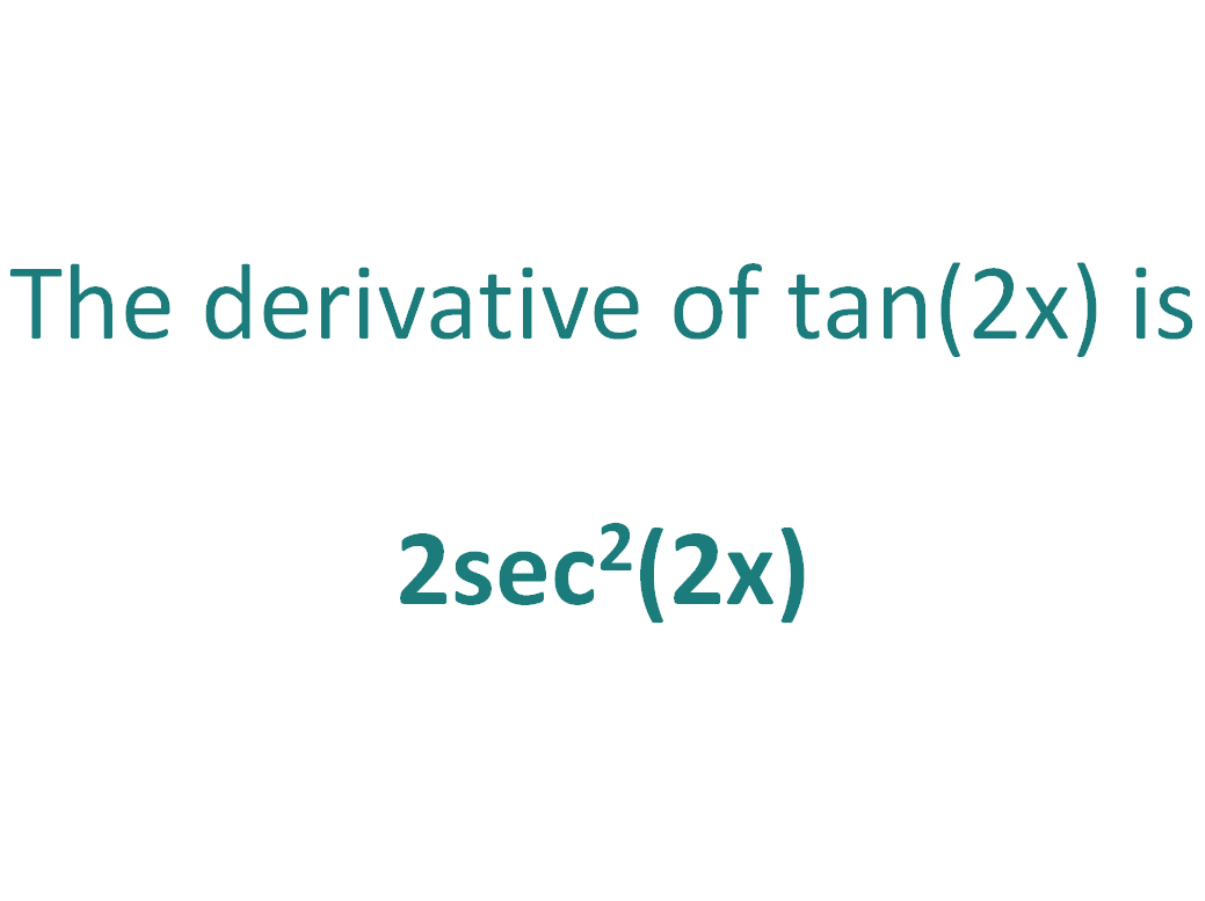



The Derivative Of Tan 2x Derivativeit
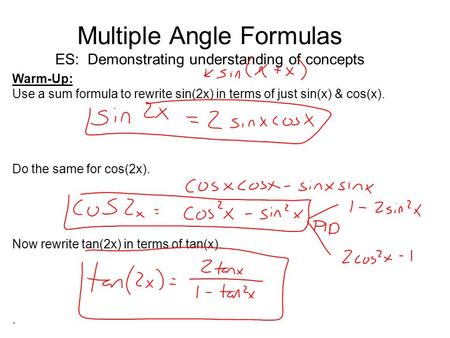
Let, y = tan(2x) let 2x=t (1) then, y = tant(2) dwrtx eq (1) 2 = dt/dx dwrtt eq(2) dy/dt = secmath^2(t)/math by chain rule ofTan 2x = 2 tan x/1 tan2 x = 2 cot x/ cot2 x 1 = 2/cot x – tan x tangent doubleangle identity can be accomplished by applying the same methods, instead use the sum identity for tangent, first • Note sin 2x ≠ 2 sin x;Tan2x Formula is also known as the double angle function of tangent Let's look into the double angle function of tangent ie, tan2x Formula is as shown below tan 2x = 2tan x / 1−tan2x where, tan x = Opposite Side / Adjacent Side tan 2x = Double angle function of tan x tan 2 x = Square funtion of tan x ie, tan 2 x = (tan x) 2



1
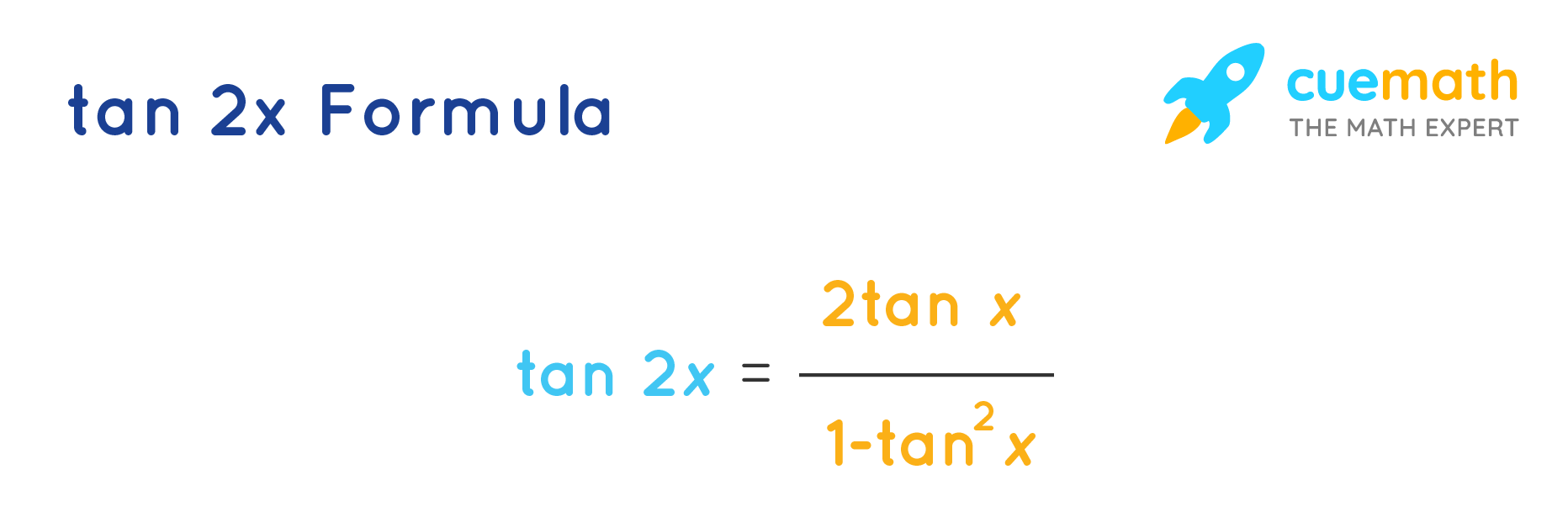



Tan 2x Formula What Is Tan 2x Formula Examples
Equations Tiger Algebra gives you not only the answers, but also the complete step by step method for solving your equations sec^2xtan^2x so that you understand better Introduction to Tan double angle formula let's look at trigonometric formulae also called as the double angle formulae having double angles Derive Double Angle Formulae for Tan 2 Theta \(Tan 2x =\frac{2tan x}{1tan^{2}x} \) let's recall the addition formula \(tan(ab) =\frac{ tan a tan b }{1 tan a tanb}\) So, for this let a = b , it becomesTan 2x ≠ 2 tan x




Find The Derivative Of The Given Function Y Tan 2x 1 Cot 2x I Tried Converting The Original Function In Terms Of Sin And Cos But It Was Still Too Complicated To Be Called Simplified




Limit Of Tan 6x 2x Calculus 1 Calculus Math Tutorials Email Subject Lines
How to find the integral of tan(2x)In this tutorial we go through the steps to find the integral of tangent(2x) using the usubstitution integration methodClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Find the general solution of the equation sec^2 2x = 1 tan 2xDerivative of (tan(2x))^7 Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving process




Tan Graphs Circular Functions




Sorry For This Question But Is Tan 2x 3 The Same With Tan 2x 3 Or No Because My Classmates Differentiated This By Changing Tan 2x 3 To Tan 2x 3 Because I Don T Know Any
1tan^2(x) = 1 (sin2x)/(cos2x) = cos2x sin2x/cos2x = cos 2x/cos2x is a posibly 'simplified' version in that it has been boiled down to only cosinesGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Piece of cake Unlock StepbyStep Extended Keyboard Examples



Tanx Tan2x Tan3x Tanxtan2xtan3x




Which Of The Following Are Solutions To 2tanx 1 Tan 2x Sqrt 3 Check All That Apply Options Are In Brainly Com
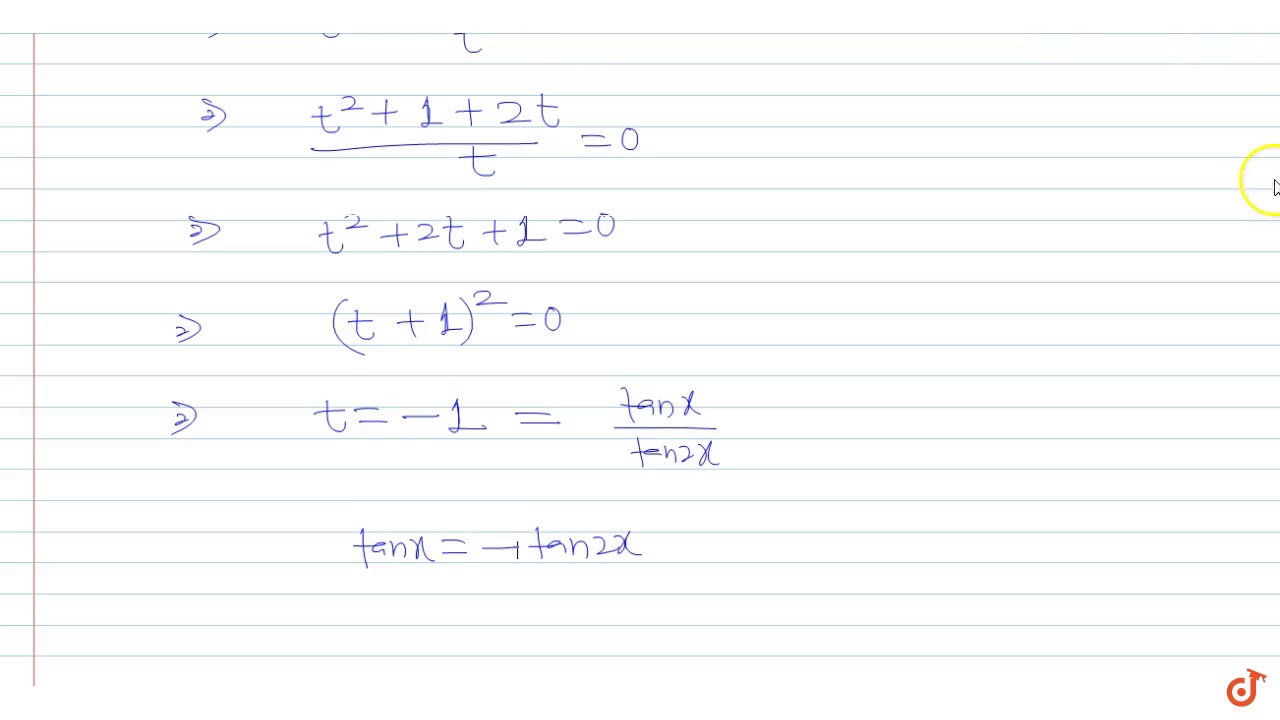



The General Solution Of The Equation Tanx Tan2x Tan2x Tanx 2 0 Is Youtube
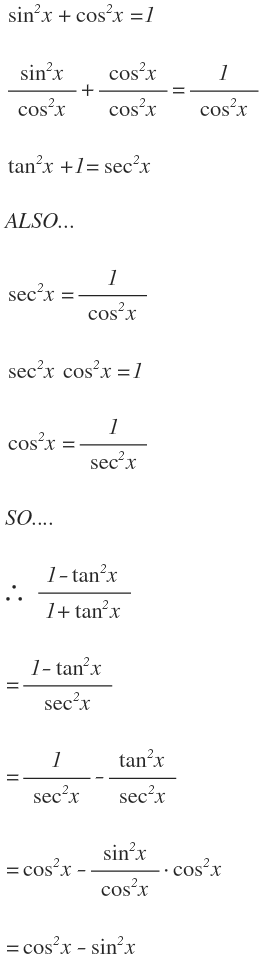



How Do You Simplify 1 Tan 2 X 1 Tan 2 X Socratic




Integrate Tan X Tan 2x Tan 3x Dx Maths Integrals Meritnation Com




Chứng Minh Cac đẳng Thức Lượng Giac Tan 2x Sin 2x Tan 2x Sin 2x Toan Học Lớp 10 Bai Tập Toan Học Lớp 10 Giải Bai Tập Toan Học Lớp 10



Phương Trinh Tanx 1 Tan2x 1 2cot X Pi 4 Co Một Họ Nghiệm La Vietjack Com




Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x If Sin X 5 13 Gauthmath
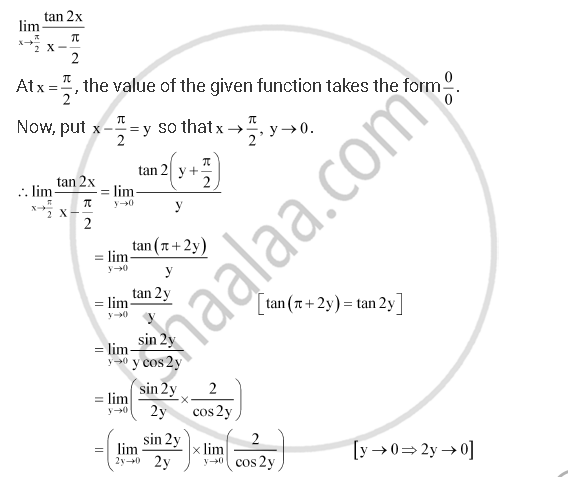



Evaluate The Given Limit Lim X Pi 2 Tan 2x X Pi 2 Mathematics Shaalaa Com
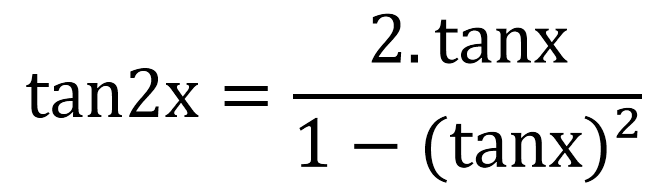



Tan2x Acilimi Pow Bylge




Solution Solve For X In The Given Equation Arc Tan 2x Arctan X P 4




Cbse Class 11 Sin 2x Sin 3x Cos 2x Cos 3x Tan 2x Tan 3x Offered By Unacademy



1



What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora
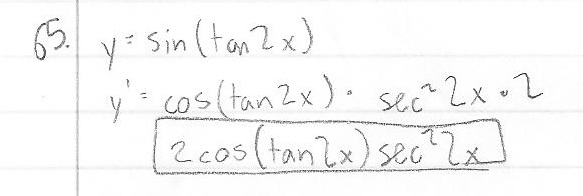



Tan2x Sec2x ただの悪魔の画像



Solution Determine The Period Of Y Tan 2x



Math Problems Simplifying With Trigonometry Identities And Then Integration
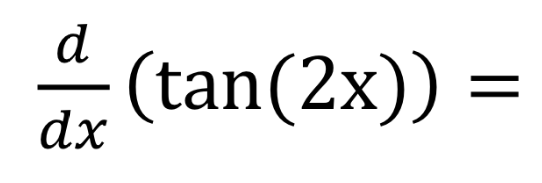



D Dx Tan 2x Chegg Com




Cos 2x1 Tan 2x A 1 2 Sin 2x B 3 Cos 2x Sin Gauthmath
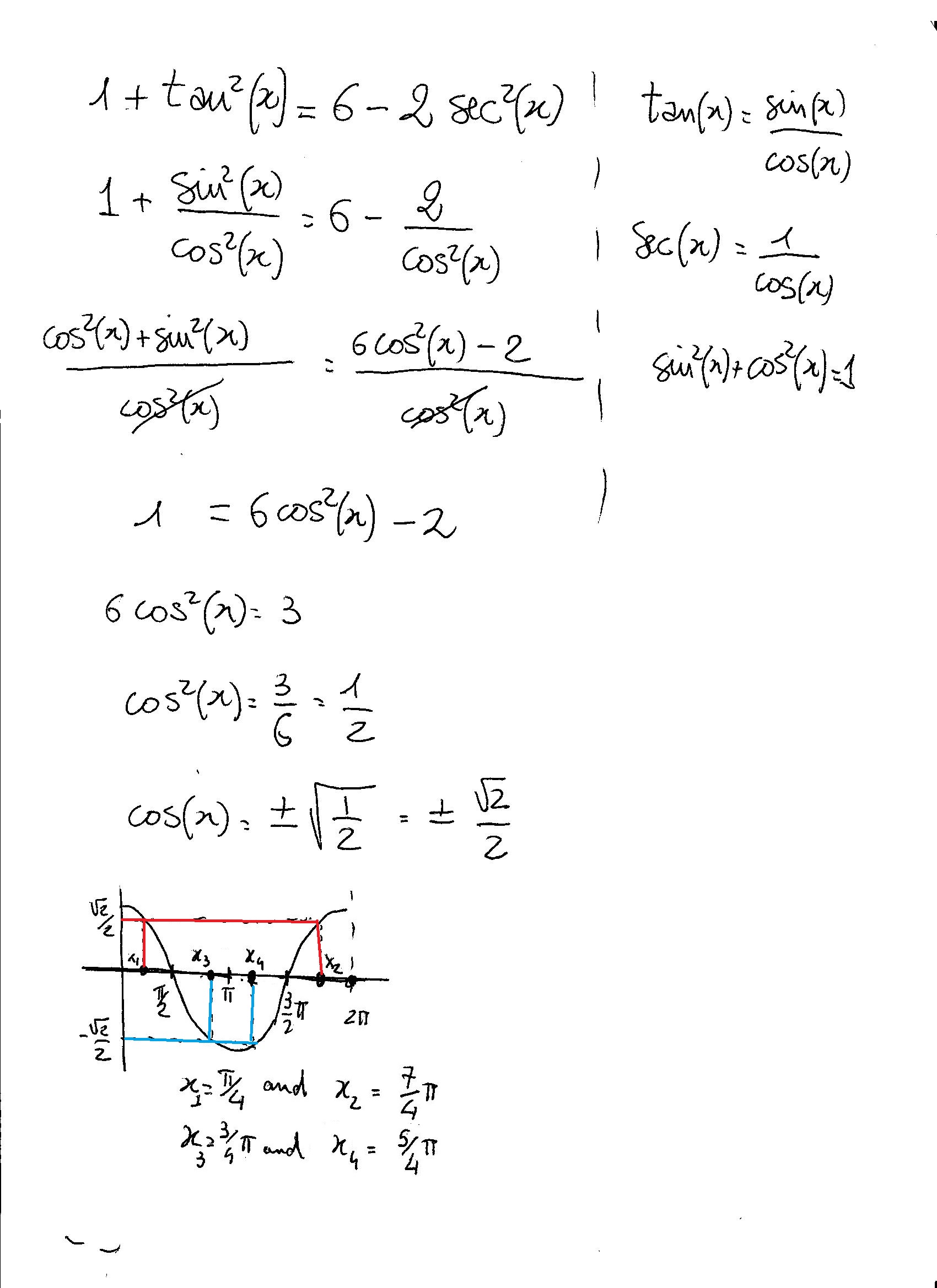



How Do You Solve 1 Tan 2x 6 2sec 2x Socratic




What Is Integral Of Sin2x Tan2x Quora



3
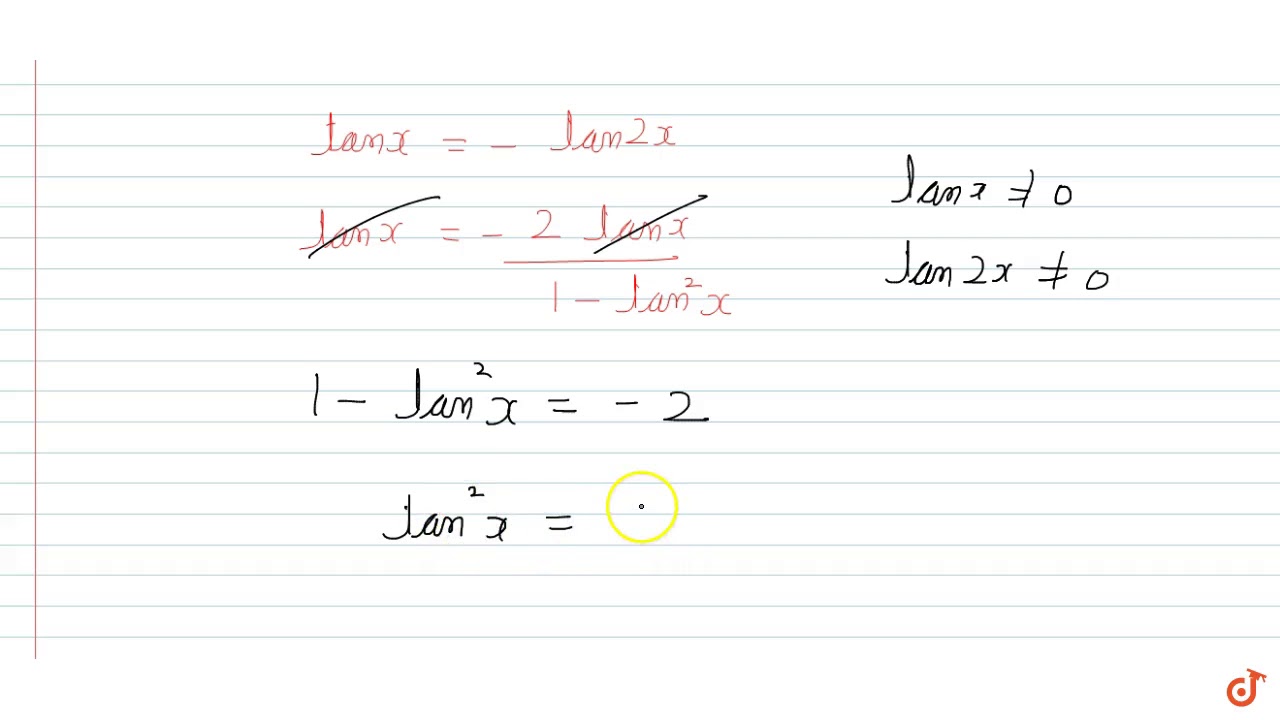



The General Solution Of The Equation Tanx Tan 2x Tan 2x Tanx 2 0 Is Youtube




Example 22 Find Derivative Of Tan 2x 3 Chapter 5 Class 12
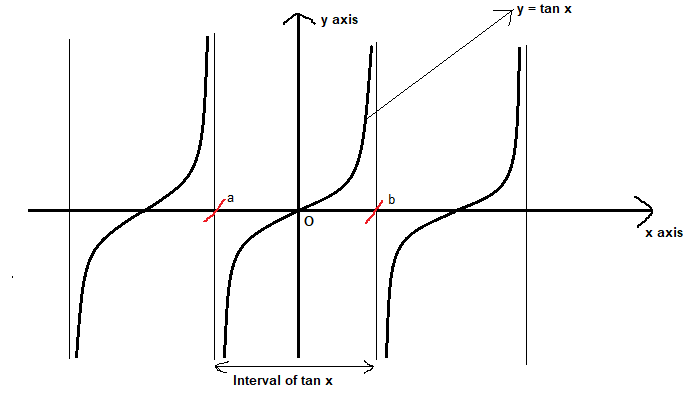



Find The Period Of Tan 2x Class 10 Maths Cbse




Nhung Cong Thuc Luong Giac Co Ban




Tan 2xの不定積分で Sin 2から1 Cos 2xになるのはなぜでしょうか Clear




Diketahui Sin X A Nilai Tan 2x Adalah Brainly Co Id




Tan 2x Cot 2x Plsss Give Brainly In




Mathematics Post Your Doubts Here Page 405 Xtremepapers



Evaluate Limx 0 X 2 Tan 2x Tan X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Derivative Of Tan 2x




Tan 2x 3 0 Untuk 0 X 360 Mas Dayat




Find Integral Of Tanx 1 Tanx Tan 2 X
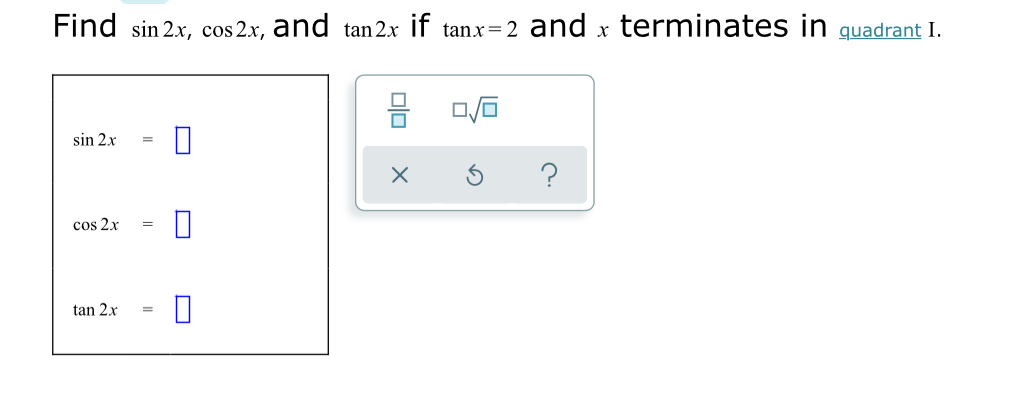



Answered Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan2x If Bartleby



Solved Consider The Possible Identity Tan 2x Cos 2x 1 Cos 2x Sec 2x A State Any Non Permissible Values B Attempt To Verify Possible Identity Course Hero




Solve Tan 2 X 1 0 Yahoo Answers Noha Matthieu Lire Un Livre




Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x If Cos X 3 5 And Gauthmath




Ex 3 4 8 Find General Solution Of Sec 2 2x 1 Tan 2x Teachoo
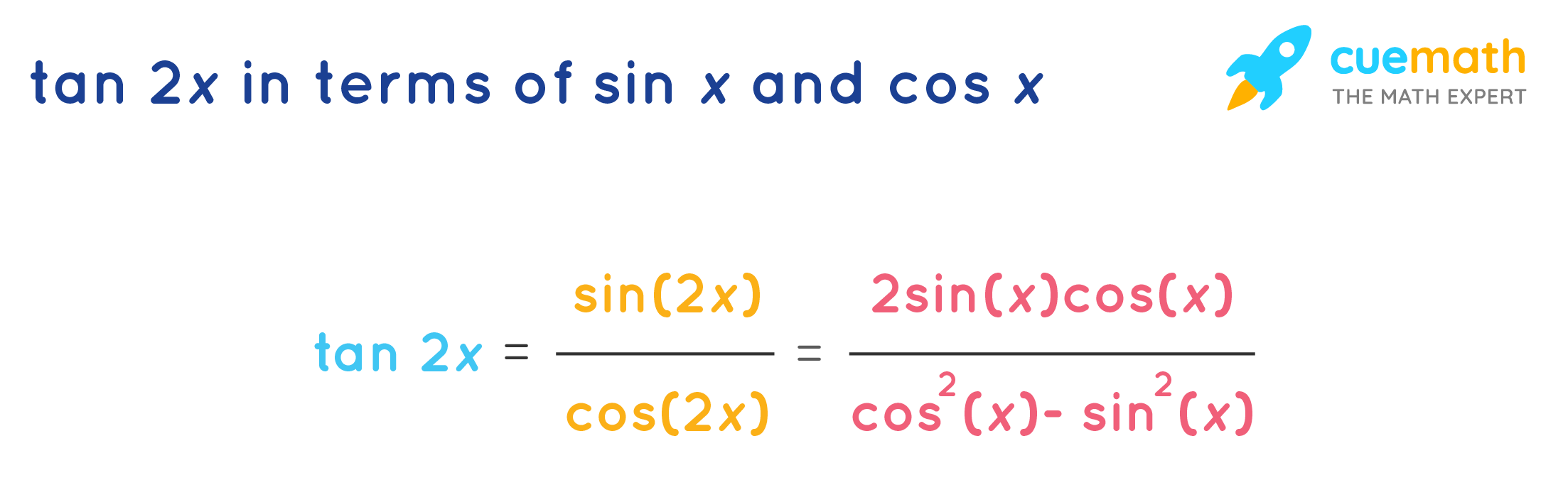



Tan 2x Formula What Is Tan 2x Formula Examples



If Tan X Cot X 2 Find The Value Of Tan 2x Cot 2x




Dopl3r Com Memes 3 Sec2x 1 Cos 2 X Tan 2x Tan X Esus The An Is Always 5




Lim X 0 Log Tan 2x Tan 2 2x




Cbse Class 11 Sin 2x Sin 3x Cos 2x Cos 3x Tan 2x Tan 3x Offered By Unacademy




Find Dy Dx 1 Tan 2x 1 Cot 2x Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com




The General Solution Of Tanx Tan2x Tan3x Tanx Tan2x Tan3x




Tangent For Sum Of Double Angle Shortmath




Solve Tan 2x Tanx 0




Integrate Tanx Tan 2x Tan3x Dx Maths Integrals Meritnation Com




Ex 6 3 Q10 F X Tan 2x Sketch The Graphs Of The Following Functions




Soal Persamaantan Tan 2x 30 Sqrt3quad Untuk 0 0




D Cotx Tanx Dx Cot X Tan X 1 2sin 2x 04 2 2 Sec 2x Tan 2 Scholr
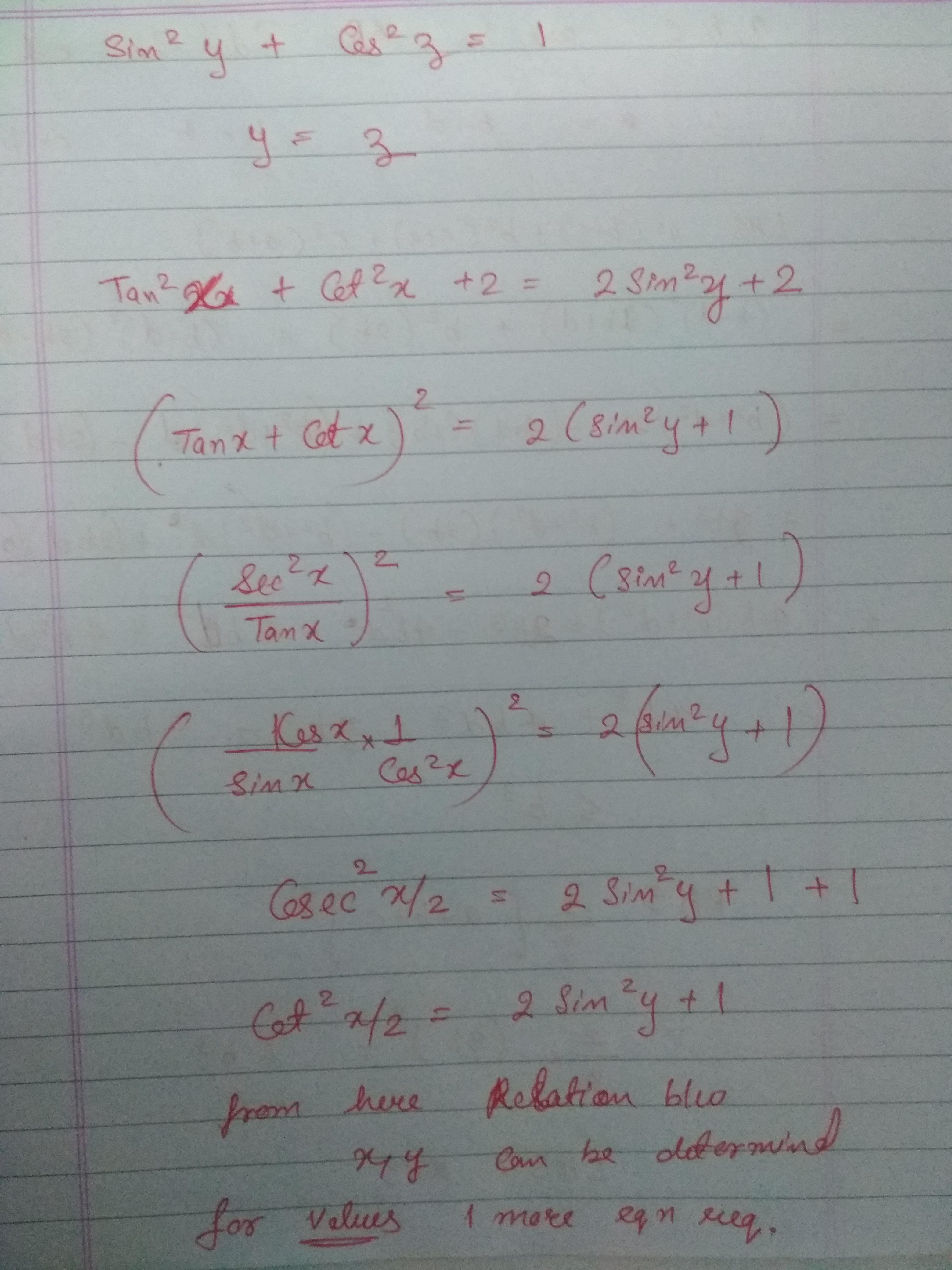



Solve For X Y And Z If Tan 2x Cot 2x 2sin 2y And Sin 2y Cos 2z 1 Askiitians
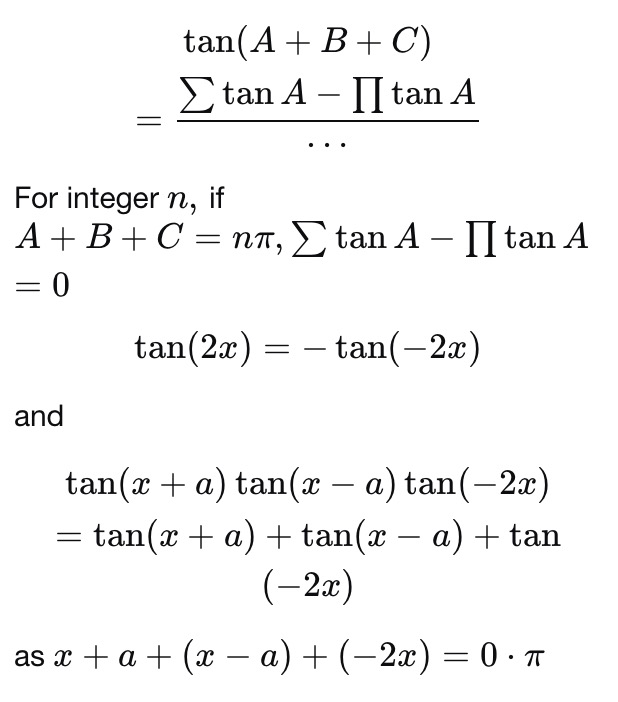



Please Integrate This And Send Me The Solution Maths Doubts Goiit Com




bestpictjcry Tan 2x Tan 2x




1 Tan 2x Sin 2x Tan 2x Sin 2x 2 Sin 4x Cos 4x 2s Gauthmath



How Does One Verify Cos 2x Sin 2x 1 Tan 2x Cos 2x Socratic








Solution Solve For X In The Given Equation Arc Tan 2x Arctan X P



Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x From The Given Information Image Select The Correct Answer Ppt Download




Q 12 Solve Sec 2x 1 Tan 2x




1 Point If Tan X 1 3 Cosx 0 Then Sin 2x Cos 2x Homeworklib




Solved Sketch The Graph Of The Following Functions Y Tan 2x Y Self Study 365



Sketch The Graphs Of The Following Functions F X Tan 2x Mathematics Shaalaa Com
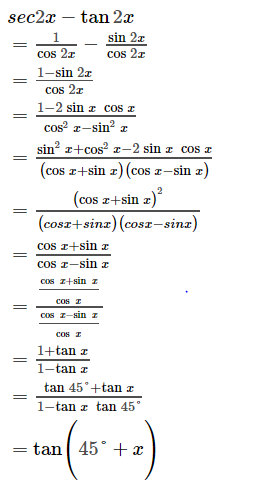



Sec2x Tan2x If0 X P 4




What Is The Integration Of Tan 2x Solution Quora



Prove That Tan 22x Tan 2x 1 Tan 22x Tan 2x Tan 3x Tan X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Ex 3 4 8 Find General Solution Of Sec 2 2x 1 Tan 2x Teachoo




Qprove That Tan X 2 Tan 2x 4 Tan 4x 8 Cot 8x Cot X Mathematics Topperlearning Com Blpusg55



Show That Tan 3x Tan 2x Tan X Tan3x Tan 2x Tan X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



6 3 2 Sketching Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions Part 1 Spm Additional Mathematics
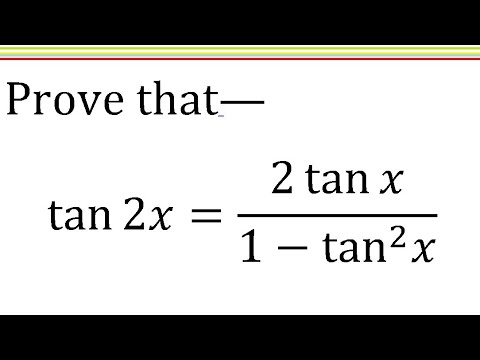



Tan2x 2tanx 1 Tan X Trigonometric Identity Solve Hindi Youtube
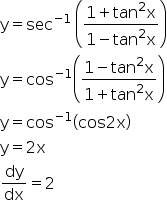



Differentiate Wrt X Sec 1 1 Tan2x 1 Tan2x Mathematics Topperlearning Com Nti7rxx




3 Sec 2x1 Cos2 X Tan 2x Tantx E Sus S Always The An 0 Om Sec Meme On Me Me
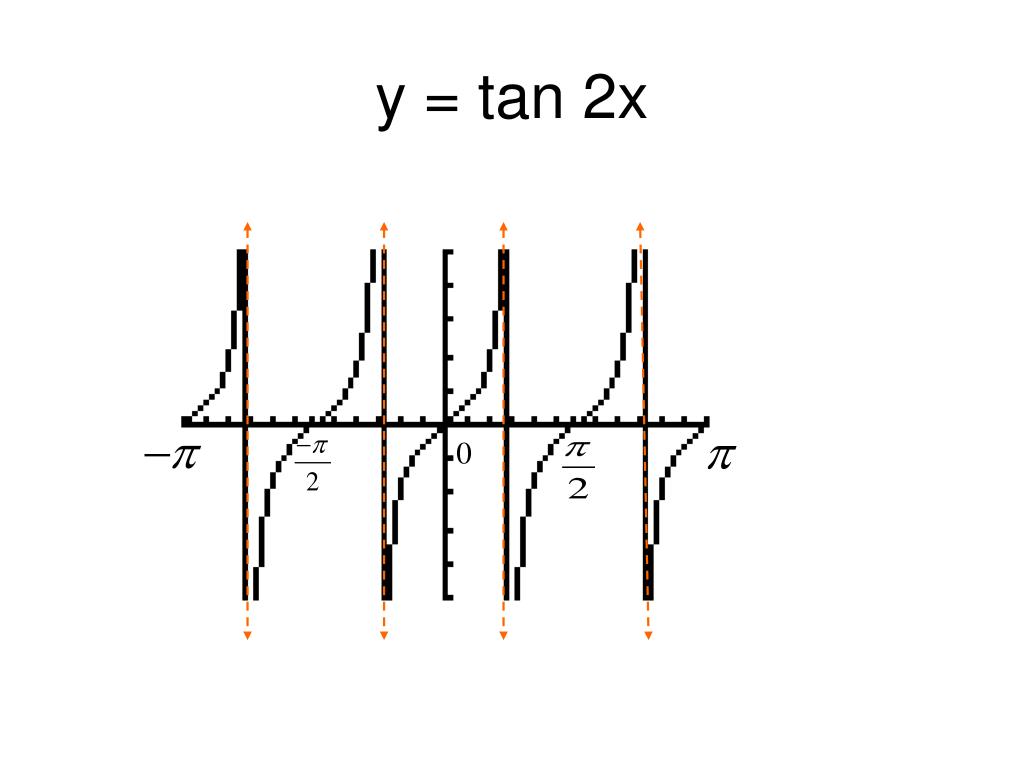



Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像



Solution Show Me The Graph Of Y Tan2x Step By Step And How To Solve Keypoints




Nhung Cong Thuc Luong Giac Co Ban




Hosszu Gazfegyverek Airsoft Rifle Awss Kac Pdw 10 Gbb Blowback Tan 2x Magazine Airsoftpro Hu




Tan 2x Cotx 0 Giải Bai Ben Cau Hỏi Hoidap247 Com




Integrate Tan 2x By Parts



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿