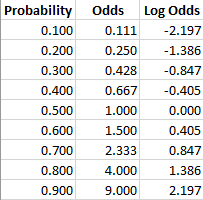
Odds Ratio (OR) measures the association between an outcome and a treatment/exposure Or in other words, a comparison of an outcome given two different groups (exposure vs absence of exposure) OR is a comparison of two odds the odds of an outcome occurring given a treatment compared to the odds of the outcome occurring without the treatmentDecimal odds represent the amount one wins for every $1 wageredOct 27, 17 · So, in this example, if the probability of the event occurring = 080, then the odds are 080 / (1080) = 080/0 = 4 (ie, 4 to 1) If a race horse runs 100 races and wins 25 times and loses the other 75 times, the probability of winning is 25/100 = 025 or 25%, but the odds of the horse winning are 25/75 = 0333 or 1 win to 3 loses
Log Odds Definition And Worked Statistics Problems
Log odds versus odds ratio
Log odds versus odds ratio-Aug 26, · Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to noneventsSep 02, · The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal


Odds Vs Probability Vs Chance Data Science Central
Dec 07, · Fractional odds are sometimes called British odds or traditional odds and are sometimes written as a fraction, such as 6/1, or expressed as a ratio, like sixtoone Decimal odds represents theDec 03, 18 · When the Odds ratio is above 1 and below 2, the likelihood of having the event is represented as XX % higher odds (where XX % is Odds ratio 1) That means that if odds ratio is 124, the likelihood of having the outcome is 24% higher (124 – 1 = 024 ie 24%) than the comparison groupMar 16, 21 · In statistics, an odds ratio tells us the ratio of the odds of an event occurring in a treatment group to the odds of an event occurring in a control group Odds ratios appear most often in logistic regression, which is a method we use to fit a regression model that has one or more predictor variables and a binary response variable
Oct 24, · Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3 againstApr 27, 21 · The term (Intercept) is an odds for the response Yi when Di=0 and Xi=0Depending the encoding, the other term(s) will represent odds ratios for the response for the specific (nonzero) levels of Di compared to 0 If Xi is continuous, the odds ratio is a ratio fo odds for groups differing by 1 unit in XiAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% = 01% x 10), more than 10 times higher
An odds ratio of 112 means the odds of having eaten lettuce were 11 times higher among casepatients than controls Because the odds ratio is greater than 10, lettuce might be a risk factor for illness after the luncheon The magnitude of the odds ratio suggests a strong associationTherefore, the odds of rolling four on a dice are 1/5 or % Odds Ratio (OR) is a measure of association between exposure and an outcome The OR represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposure Important points about Odds ratioOct , 18 · Summary Our theoretical Odds Ratio is 0319 with a CI(0, 041), which is close to the true Odds ratio, 03This indicates if the undergraduate students are from the school in prestige 3 or 4, the chances of them getting in graduate school is 38% that of the students from prestige 1 or 2 undergraduate schools


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Solved Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com
Dec 14, 14 · A highly simplified example illustrates this Suppose that 18 out of patients (90 percent probability, odds of 91) in an experiment lost weight while using diet A, while 16 out of (80 percent, odds of 41) lost weight using diet B The relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1125, while the odds ratio is about 225Jul 01, 17 · Odds ratio in this example is found to be hight () (PJul 27, · Here's why this works, roughly one out of 11 million people will die by a plane crash The odds of that occurring is 1 divided by 11 million minus the one unfortunate soul The risk is 1 divided by the full 11 million Either provide you a similar number with which you can formulate risk


The Difference Between Probability And Odds



Underwriting Analysis For Fair Lending Using Logistic Regression Odds Ratio Vs Marginal Effects Premier Insights
This StatQuest covers those subjects so that you can understand the statiThe odds aren't as odd as you might think, and the log of the odds is even simpler!Jul 11, 16 · The odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event in the Treatment group to the odds of an event in the control group The term 'Odds' is commonplace, but not always clear, and often used inappropriately The odds of an event is the number of events / the number of nonevents



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table


9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science
Aug 07, 14 · Like we did with the risk, we can calculate the ratio of the odds of the two groups to get the odds ratio (OR), which gives us an idea of how much more likely is the event to occur in one group than the other As you can see, they are similar but different concepts In both cases, the null value is oneFeb 25, · Why are relative probability contrasts so often represented using relative odds instead of probability ratios, when risk contrasts are represented using relative risks instead of odds ratios (calculated using incidence proportions instead of probabilities)?In video two we review / introduce the concepts of basic probability, odds, and the odds ratio and then apply them to a quick logistic regression example Un


Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



Odds Ratio Wikipedia
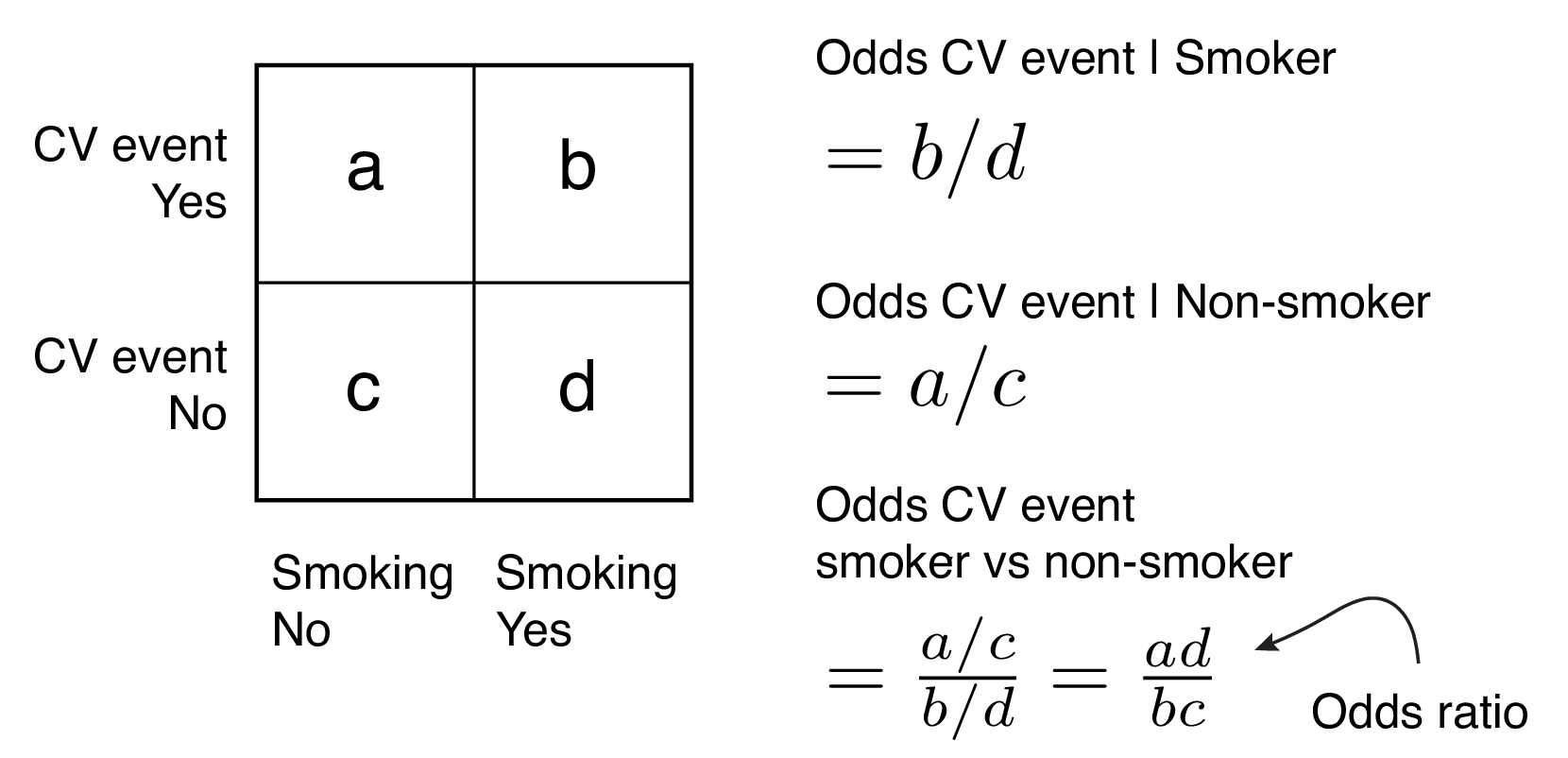
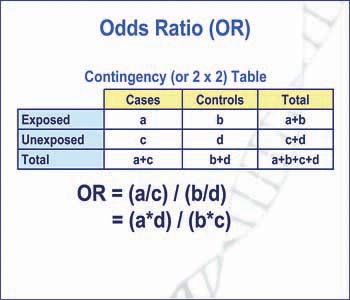
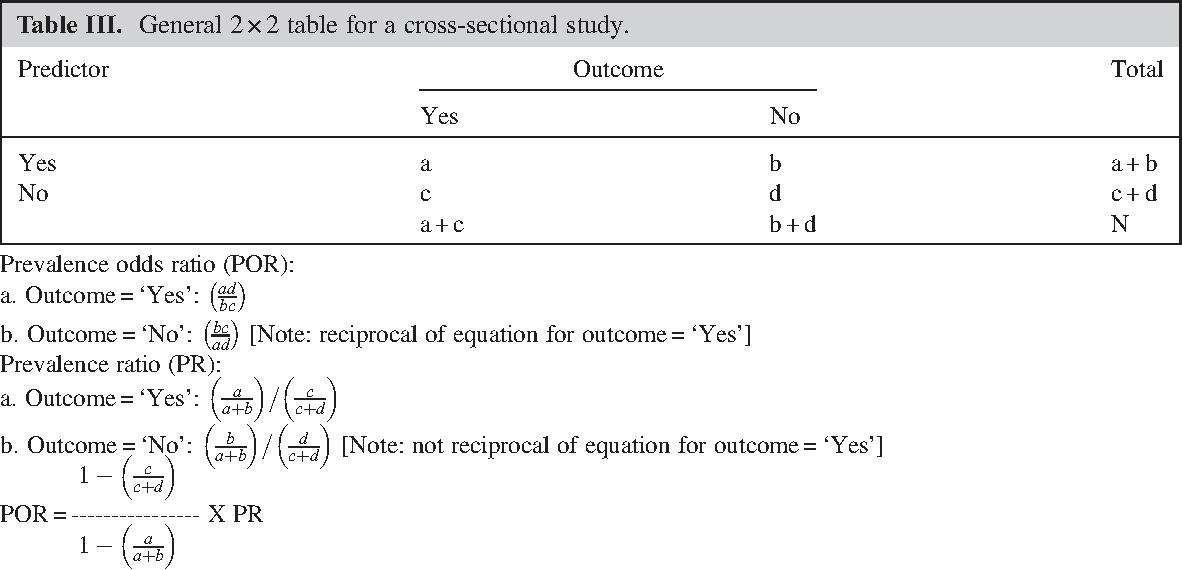
The odds ratio (OR) is a measure of how strongly an event is associated with exposure The odds ratio is a ratio of two sets of odds the odds of the event occurring in an exposed group versus the odds of the event occurring in a nonexposed group Odds ratios commonly are used to report casecontrol studiesJun 02, 09 · Odds = Probability of an Event Odds are most simply calculated as the number of events divided by the number of nonevents Odds Is Related to Probability The formal way to describe the odds is as the probability of the event divided by the probability of the nonevent So odds are the ratio of two fractions the number of events divided by the number of subjects (Dec 30, 16 · Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
Jun 01, 12 · Odds ratios work the same An odds ratio of 108 will give you an 8% increase in the odds at any value of X Likewise, the difference in the probability (or the odds) depends on the value of X So if you do decide to report the increase in probability at different values of X, you'll have to do it at low, medium, and high values of XMay 18, 12 · Odds ratio An odds ratio (OR) is another measure of association that quantifies the relationship between an exposure with two categories and health outcome Referring to the four cells in Table 315, the odds ratio is calculated as Odds ratio = (Feb 27, · For example, if odds are 3/1 for the Cowboys this Sunday, then it is three times more likely that they will lose than win Odds of 31 indicate that if you bet $100, you will win $400, the original amount of your bet plus the profit Odds of 13 will win you $33 on a $100 bet, or $133



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube
The ratio of the odds for female to the odds for male is (32/77)/(17/74) = (32*74)/(77*17) = 1809 So the odds for males are 17 to 74, the odds for females are 32 to 77, and the odds for female are about 81% higher than the odds for malesJul 09, 19 · Figure2 Odds as a fraction Odds should NOT be confused with Probabilities Odds are the ratio of something happening to something not happeningIn our scenario above, the odds are 4 to 6 Whereas, Probability is the ratio of something happening to everything that could happenSo in the case of our chess example, probability is 4 to 10 (as there were 10 gamesOct 07, 11 · Definition The Odds Ratio is a measure of association which compares the odds of disease of those exposed to the odds of disease those unexposed Formulae OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in the nonexposed) Example I often think food poisoning is a good scenario to consider when interpretting ORs Imagine a group of friends went out to



When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Fractional odds are the ratio of the amount (profit) won to the stake;"Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we explain the meaning of risk and odds and the difference between the twoDec 08, 18 · If an odds ratio (OR) is 1, it means there is no association between the exposure and outcome So, if the 95% confidence interval for an OR includes 1, it means the results are not statistically significant Example, exposure to colored vs white Christmas lights was associated with an increase in jocularity score, OR = 12 (95%CI )



Adjusted Odds Ratio Definition Examples



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
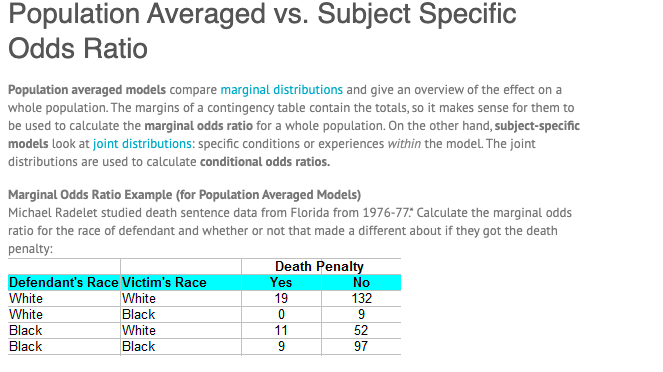
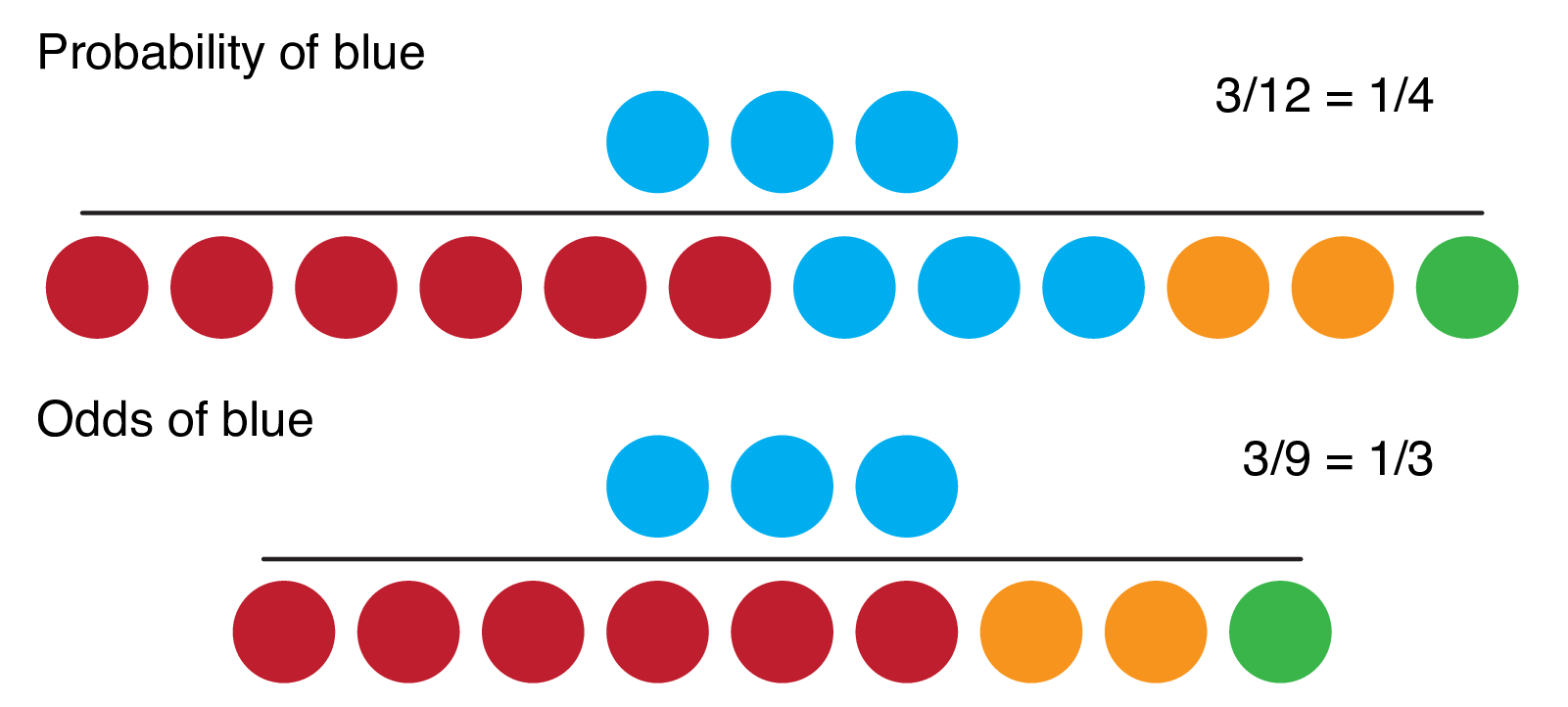
The point estimate of the oddsratio is 118 and its 95% CI is (, ), based on the CaseControl (Odds Ratio) row below The odds of death penalty are 118 times as high for white defendants as they are for black defendants Recall that a null hypothesis that oddsratio = 1 means that the variables are independentOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)Mar 02, · The odds ratio for picking a red ball compared to a green ball is calculated as Odds (red) / Odds (green) = 4 / 025 = 16 Thus, the odds of picking a red ball are 16 times larger than the odds of picking a green ball When Are Odds Ratios Used in the Real World?



Log Odds Definition And Worked Statistics Problems


Odds Vs Probability Vs Chance Data Science Central
Exactly The odds ratio of picking blue in B relative to A is 6 Yet we understand intuitively (and from the RR) that you are only 3 times as likely to pick blue in this situation, not 6 times as likelyEnglishwise, they are correct it is the odds and the odds are based on a ratio calculation It is not, however, the odds ratio that is talked about when results are reported The odds ratio when results are reported refers to the ratio of two odds or, if you prefer, the ratio of two odds ratios That is, let us write o(Xb) = exp(Xb)Dec 14, 15 · But the odds ratio makes no sense (to nonstatisticians) The odd ratio of picking blue in A relative to B is 016 What!?



Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy


Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World
The odds ratio is a way of comparing whether the odds of a certain outcome is the same for two different groups (9) The odds ratio is simply the ratio between the following two ratios The ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who died, and the ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who survived



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal


What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science



Crude Odds Ratios Cor And Adjusted Odds Ratio Aor And Their 95 Download Table



Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research


Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk



Useful Concept For Medical Healthcare Data Risk Prediction



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference The Journal Of Family Practice Pre School Books Clinical Trials Data Science



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio On The Backpack And Back Pain Study Massage And Fitness Magazine


Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
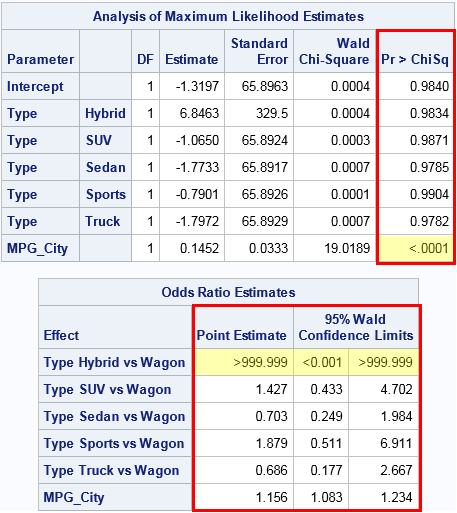


Formats For P Values And Odds Ratios In Sas The Do Loop



Odds Ratio Article



Chi Square And Odds Ratios Ppt Video Online Download


Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsterm


Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube


Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream
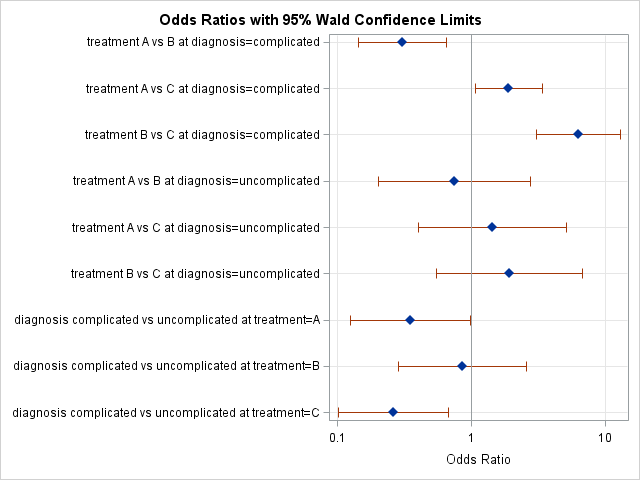


Odds Ratio Plots With A Logarithmic Scale In Sas The Do Loop



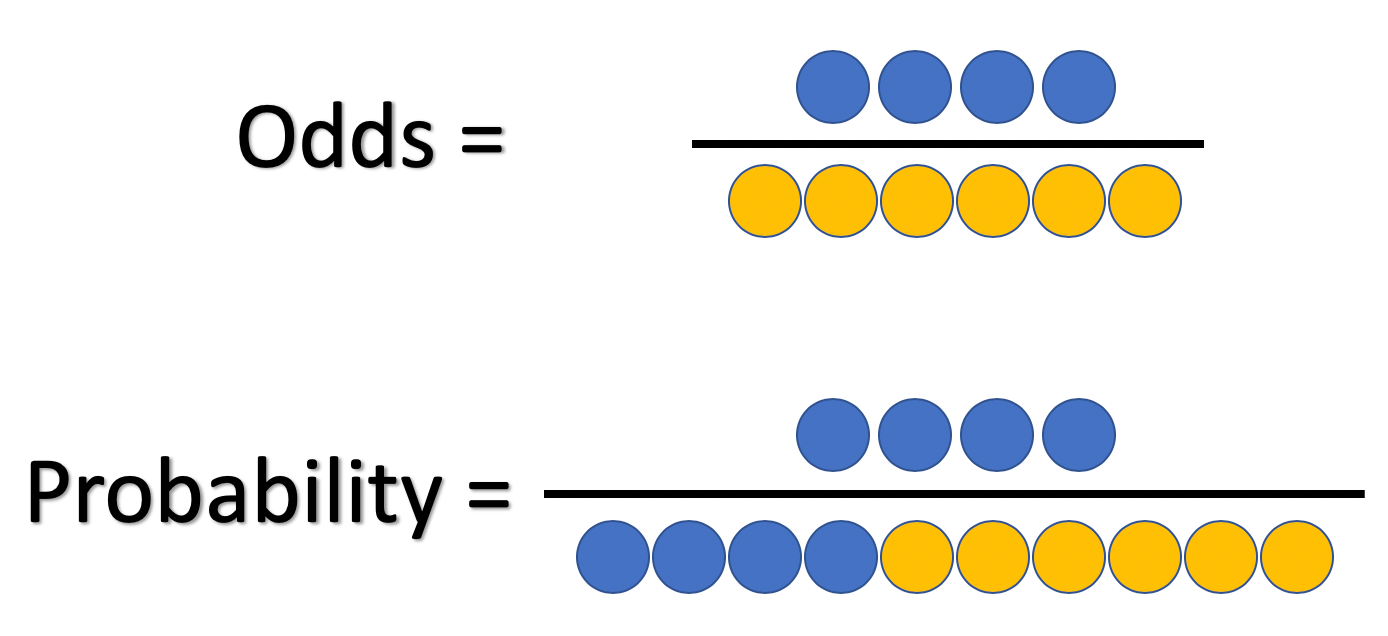
Plus An Chance Percentage Circumcised Than 1 Indicates To The Clause Or Else As It Is Odds Vs Odds Ratio



Volcano Plot From Univariate Analysis Depicting Odds Ratio Versus Download Scientific Diagram



Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training


Population Averaged Vs Subject Specific Odds Rati Chegg Com



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Likelihood Ratio And Odds Ratio Slope Values Represent Odds As Shown Download Scientific Diagram



What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science



Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club



Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



Odds Ratio Wikipedia
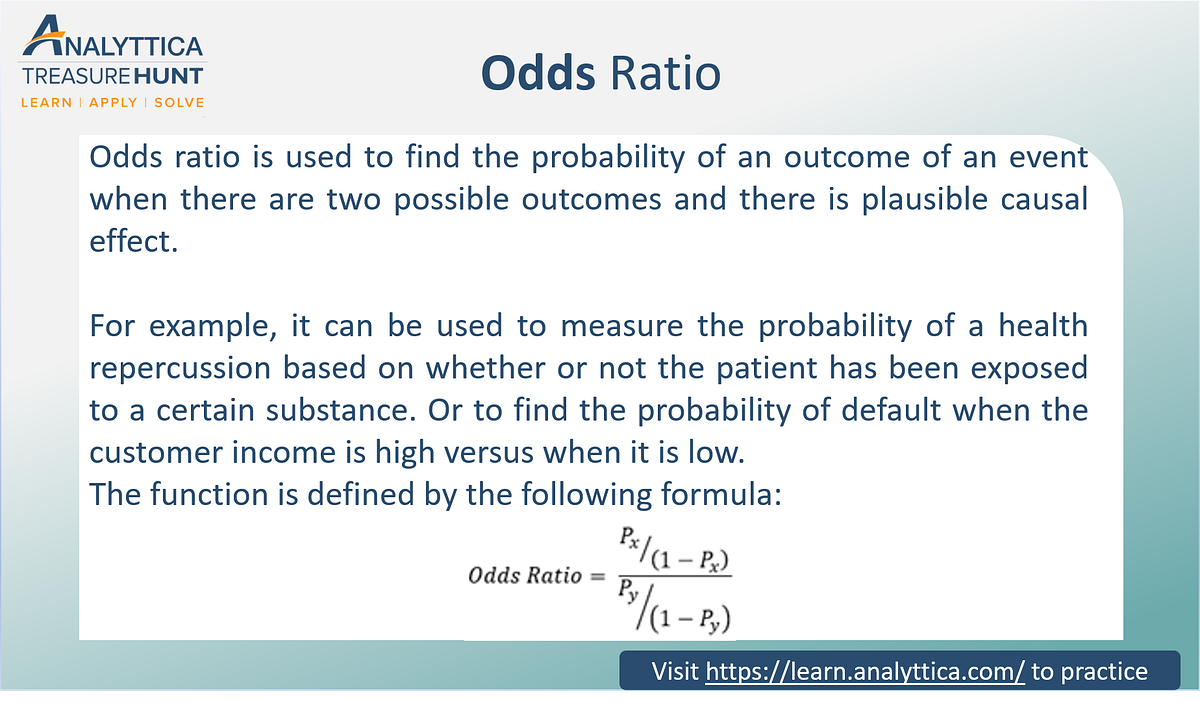


Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium



What Is A Pooled Odds Ratio Quora


Pdf Prevalence Odds Ratio Versus Prevalence Ratio Choice Comes With Consequences Semantic Scholar



Graph Of Odds Ratio Versus Sleep Image Eurekalert Science News



Solved Logistic Regression With Multiple Outcome Variables Jmp User Community



Math3010 Week 6



How To Interpret The Weights In Logistic Regression By Mubarak Bajwa Medium


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International


Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Figure 6 Random Effects Model Meta Analysis Of Relative Odds Ratio Of Icd Vs No Icd For Arrhythmic Death Between Women And Men Assessment On Implantable Defibrillators And The Evidence For Primary
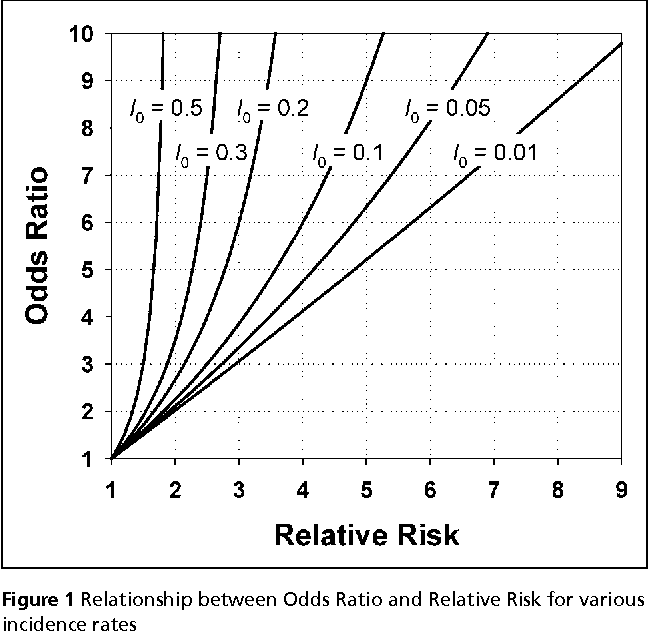


Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube
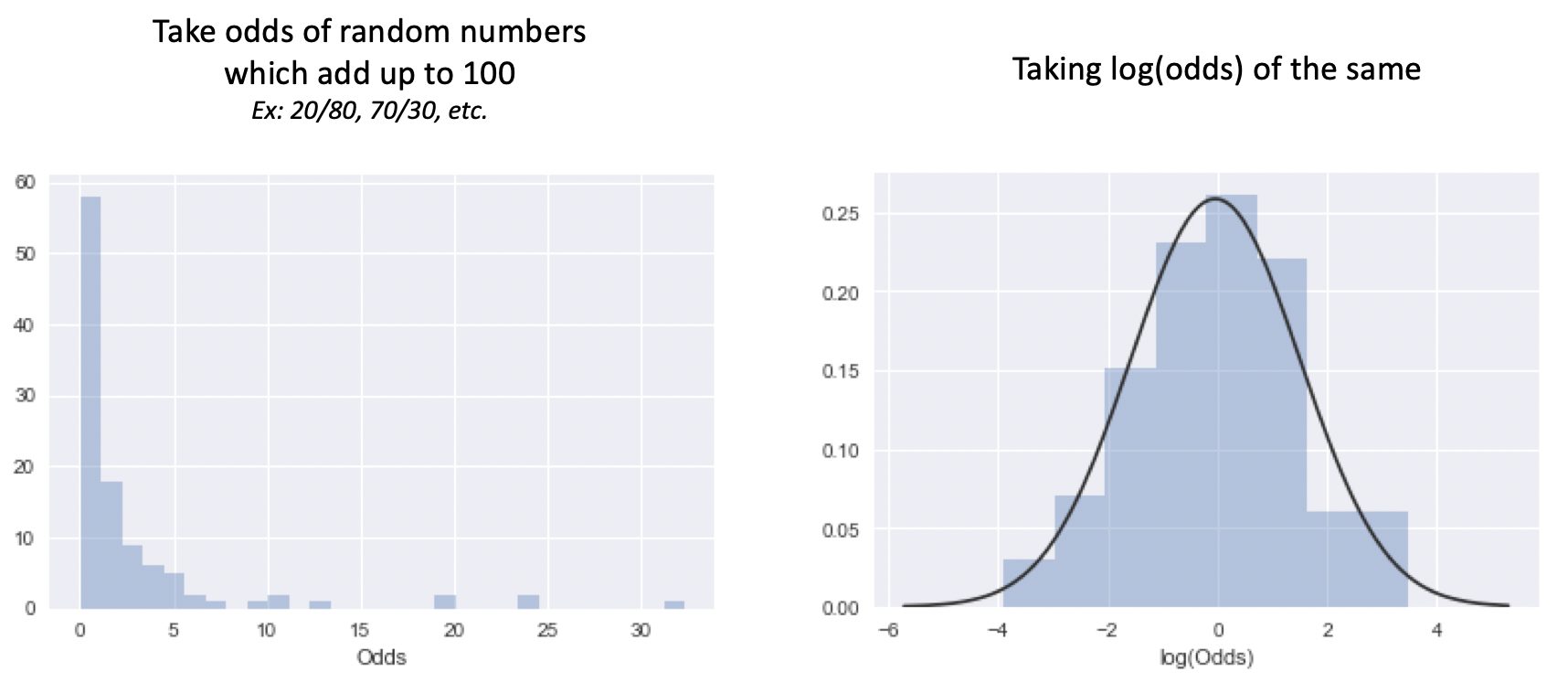


What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk


Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout
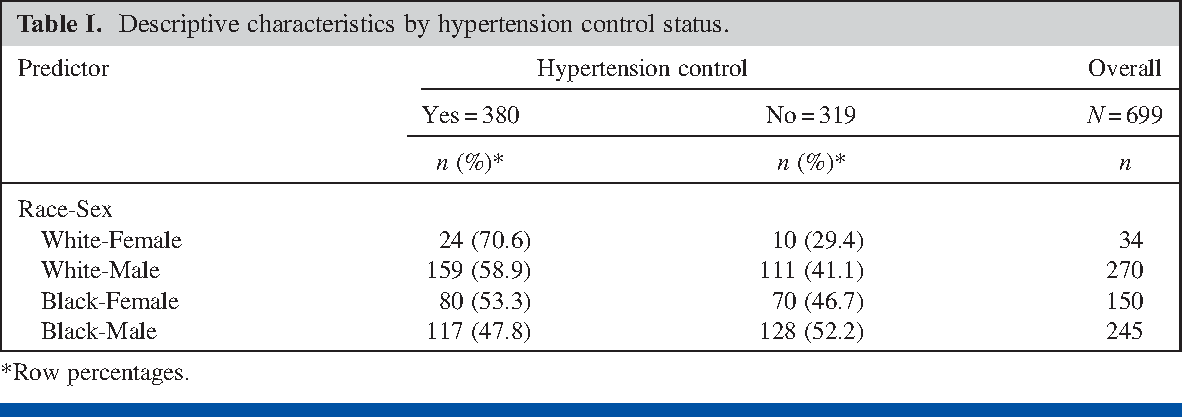


Pdf Prevalence Odds Ratio Versus Prevalence Ratio Choice Comes With Consequences Semantic Scholar


Odds Likelihood Ratios Guide To Diagnostic Tests



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence


Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



The Odds Ratios Ors Mean Difference Md With 95 Confidence Download Scientific Diagram



Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download


Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough
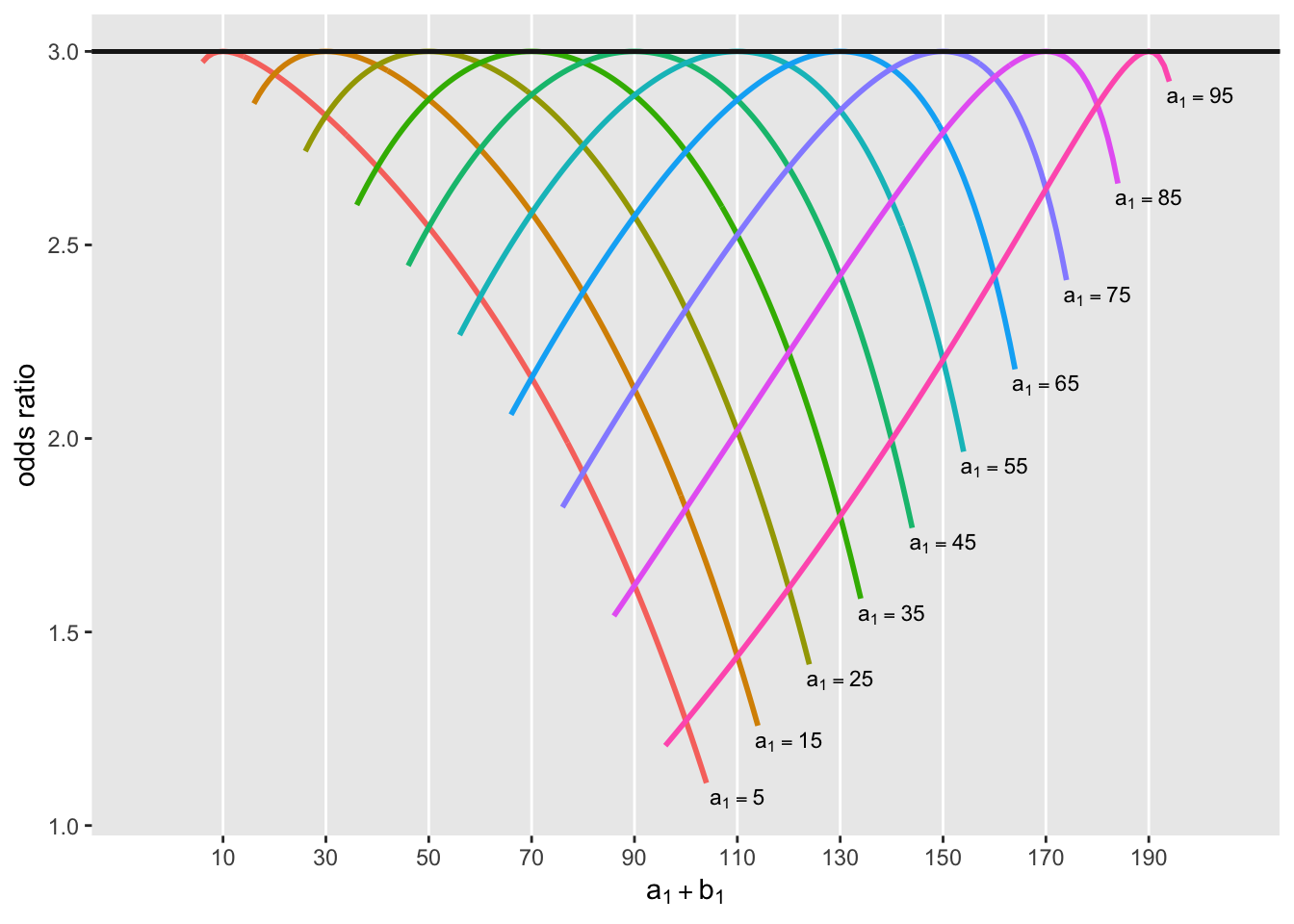


How The Odds Ratio Confounds A Brief Study In A Few Colorful Figures Our Data Generation



Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Stack Overflow



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Plotting Odds Ratio Vs Continuous Variable In Stata Stack Overflow
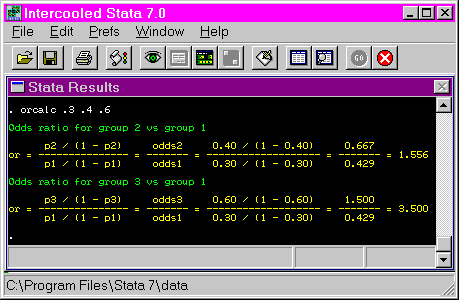


Stata Teaching Tools Odds Ratio Calculation



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
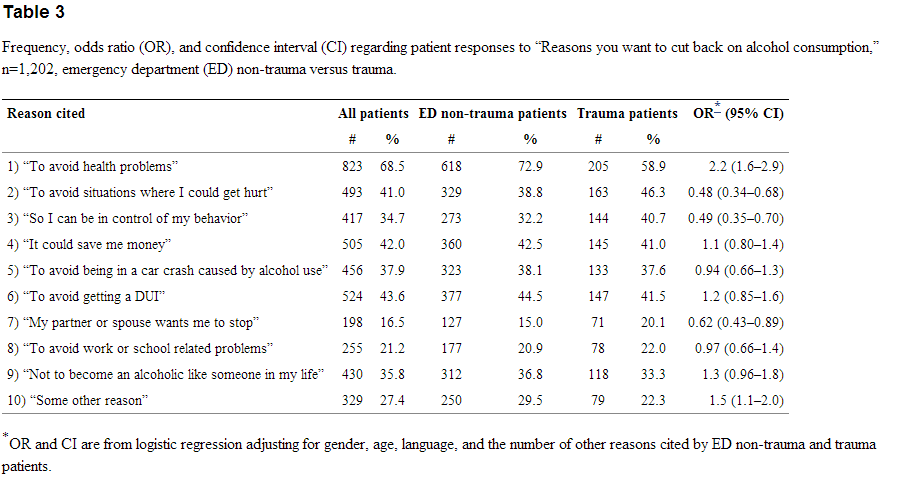


Table 3 Frequency Odds Ratio Or And Confidence Interval Ci Regarding Patient Responses To Reasons You Want To Cut Back On Alcohol Consumption N 1 2 Emergency Department Ed Non Trauma Versus Trauma The



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February
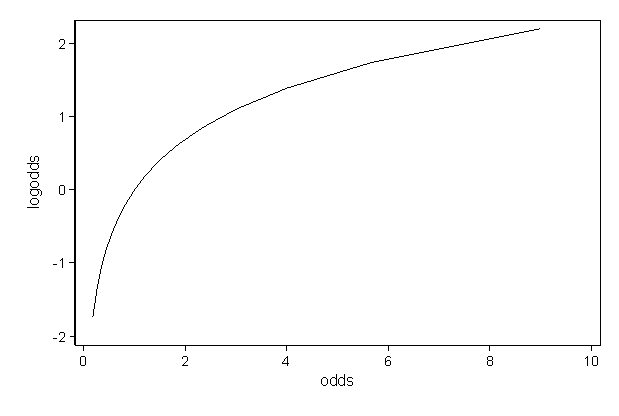


Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression



Figure 7 Random Effects Model Meta Analysis Of Relative Odds Ratio Of Icd Vs No Icd For Arrhythmic Death Between Younger And Older Subgroups Assessment On Implantable Defibrillators And The Evidence For


9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science
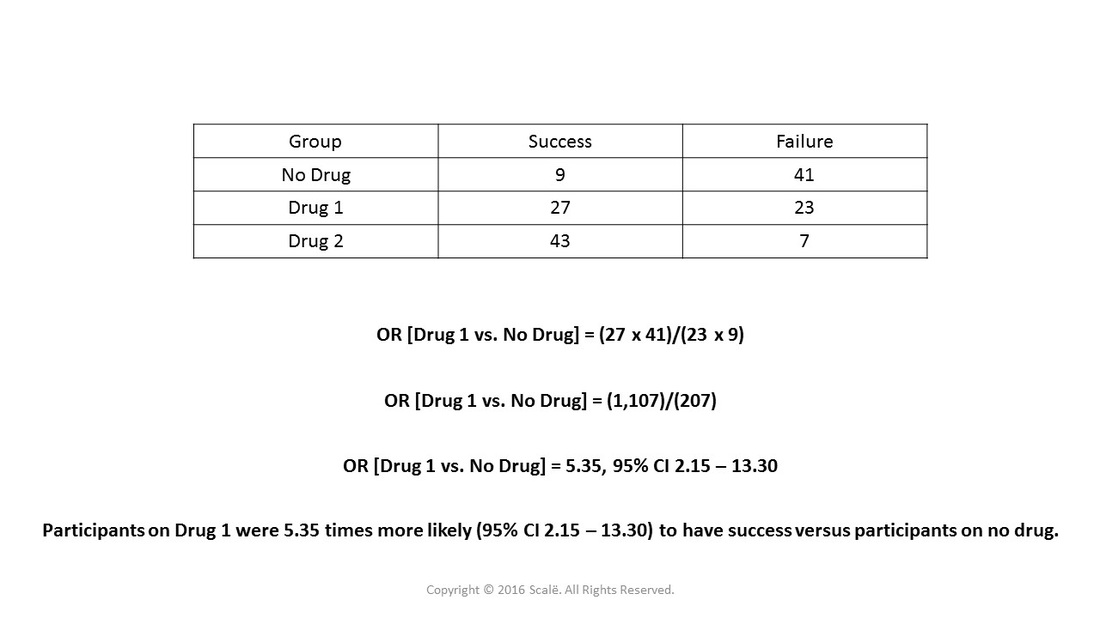


Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿